產品櫥窗
-
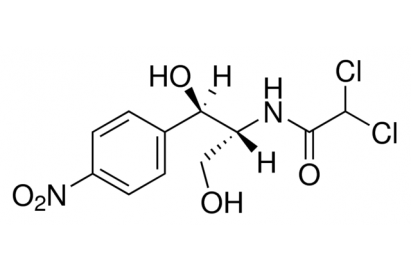
Chloramphenicol
|
產品型號:101-56-75-7 商品規格: |
 |
Selection Antibiotics. Synonym: Chloromycetin
C11H12Cl2N2O5
M.W.: 323.13
Assay: 99% Max.
Chloride (Cl): 100ppm Max.
Loss on Drying: 0.50% Max.
Cell culture tested
A white to Grayish-white or Yellowish-white Crystalline Powder
BP2002
Chloramphenicol is a synthetic antibiotic, which was first isolated from strains of Streptomyces venezuelae. It has a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Chloramphenicol inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by blocking the peptidyl transferase step (elongation inhibition). It binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit and prevents attachment of aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome. This antibiotic is often used in molecular biology applications for bacterial selection (10-20 μg/ml). The mode of resistance is inactivation of chloramphenicol (acetylation) by chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cate gene).
Stock Conc.: 10 or 34mg/mL in EtOH, Store at -20℃
Working Conc.: 20-170ug/mL
M.W.: 323.13
Assay: 99% Max.
Chloride (Cl): 100ppm Max.
Loss on Drying: 0.50% Max.
Cell culture tested
A white to Grayish-white or Yellowish-white Crystalline Powder
BP2002
Chloramphenicol is a synthetic antibiotic, which was first isolated from strains of Streptomyces venezuelae. It has a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Chloramphenicol inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by blocking the peptidyl transferase step (elongation inhibition). It binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit and prevents attachment of aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome. This antibiotic is often used in molecular biology applications for bacterial selection (10-20 μg/ml). The mode of resistance is inactivation of chloramphenicol (acetylation) by chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cate gene).
Stock Conc.: 10 or 34mg/mL in EtOH, Store at -20℃
Working Conc.: 20-170ug/mL
Store at 4-25℃.
Can store at Room Temperature.
Store at 4℃ for long term storage.
Can store at Room Temperature.
Store at 4℃ for long term storage.