產品櫥窗
-
TCEP (DTT replacement)
|
產品型號:101-51805-45-9 商品規格: |
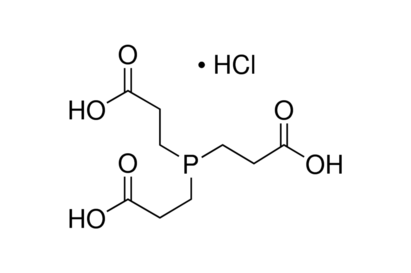 |
Reducing reagent and more stable than DTT. Synonym:Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride.
C9H15O6P•HCl
MW: 286.65
Introduction:
TCEP-HCl is a potent, versatile, odorless, thiol-free reducing agent with broad application to protein and other research involving reduction of disulfide bonds. The unique compound is easily soluble and very stable in many aqueous solutions. TCEP reduces disulfide bonds as effectively as dithiothreitol (DTT), but unlike DTT and other thiol-containing reducing agents, TCEP does not have to be removed before certain sulfhydryl-reactive crosslinking reactions.
Application:
TCEP hydrochloride is widely used as a reducing agent to reduce disulfide bonds in proteins and trans-4,5-dihydroxy-1,2-dithiane. It is involved in the reduction of sulfoxides, sulfonyl chlorides, N-oxides and azides. It plays an important role in the tissue homogenization process for RNA isolation. It acts as a chelating agent and forms complexes with various heavy metal ions such as Zn(II), Cd(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II). Furthermore, it is useful in the labeling of cysteine residues with maleimides.
La, M.; Feng, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, C. Performances of p-Aminophenol Redox Cycling by Thiols and Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine on Cysteamine-and 3-Mercaptopropionic acid-Covered Gold Electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 6985-6992.
Miralles, G.; Verdie?, P.; Puget, K.; Maurras, A.; Martinez, J.; Subra, G. Microwave-mediated reduction of disulfide bridges with supported (Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine) as resin-bound reducing agent. ACS Comb. Sci. 2013, 15 (4), 169-173.
MW: 286.65
Introduction:
TCEP-HCl is a potent, versatile, odorless, thiol-free reducing agent with broad application to protein and other research involving reduction of disulfide bonds. The unique compound is easily soluble and very stable in many aqueous solutions. TCEP reduces disulfide bonds as effectively as dithiothreitol (DTT), but unlike DTT and other thiol-containing reducing agents, TCEP does not have to be removed before certain sulfhydryl-reactive crosslinking reactions.
Application:
TCEP hydrochloride is widely used as a reducing agent to reduce disulfide bonds in proteins and trans-4,5-dihydroxy-1,2-dithiane. It is involved in the reduction of sulfoxides, sulfonyl chlorides, N-oxides and azides. It plays an important role in the tissue homogenization process for RNA isolation. It acts as a chelating agent and forms complexes with various heavy metal ions such as Zn(II), Cd(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II). Furthermore, it is useful in the labeling of cysteine residues with maleimides.
La, M.; Feng, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, C. Performances of p-Aminophenol Redox Cycling by Thiols and Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine on Cysteamine-and 3-Mercaptopropionic acid-Covered Gold Electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 6985-6992.
Miralles, G.; Verdie?, P.; Puget, K.; Maurras, A.; Martinez, J.; Subra, G. Microwave-mediated reduction of disulfide bridges with supported (Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine) as resin-bound reducing agent. ACS Comb. Sci. 2013, 15 (4), 169-173.
Store at 4℃