產品櫥窗
-
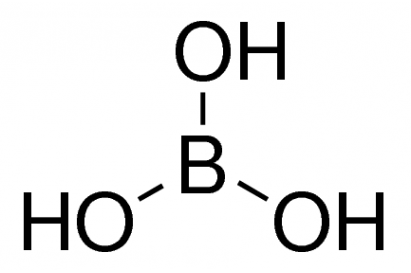
Boric Acid
|
產品型號:101-10043-35-3 商品規格: |
 |
A component of TBE Buffer for DNA Electrophoresis.
H3BO3
M.W.: 61.83
99.5% Min.
Chloride: <0.00042%
Fe: <0.00040%
Sulfate: <0.00014
Loss on Drying: <0.0048%
White crystall powder
Borate buffers are commonly used in biochemistry, with some confusion as to what reagents should be used. Boric acid has a single boron; its salt forms complex equilibria in solution, with the ion B4O7-2 being the predominant species. Many procedures do not give a method of preparation for the borate buffer intended; it is important to express the ionic strength in terms of boron molarity. One can titrate a 0.1 M solution of boric acid with sodium hydroxide to pH 9.0. If ionic strength is of no concern, titrating a solution of sodium tetraborate (borax) with HCl will also yield a buffer of pH 9.0, which contains NaCl. A 0.1 M solution of sodium tetraborate is 0.4 M in "boron ion." Several references give "recipes" for preparing borate buffers.
Boric acid dissolves in water: 1 gram in 18 mL cold water, in 4 mL boiling water, 6 mL boiling alcohol. Powdered boric acid may dissolve more slowly in water than a crystalline product, but with gentle warming will dissolve to give a clear solution.
For the most commonly used TBE buffer, with a pH of 8.3
M.W.: 61.83
99.5% Min.
Chloride: <0.00042%
Fe: <0.00040%
Sulfate: <0.00014
Loss on Drying: <0.0048%
White crystall powder
Borate buffers are commonly used in biochemistry, with some confusion as to what reagents should be used. Boric acid has a single boron; its salt forms complex equilibria in solution, with the ion B4O7-2 being the predominant species. Many procedures do not give a method of preparation for the borate buffer intended; it is important to express the ionic strength in terms of boron molarity. One can titrate a 0.1 M solution of boric acid with sodium hydroxide to pH 9.0. If ionic strength is of no concern, titrating a solution of sodium tetraborate (borax) with HCl will also yield a buffer of pH 9.0, which contains NaCl. A 0.1 M solution of sodium tetraborate is 0.4 M in "boron ion." Several references give "recipes" for preparing borate buffers.
Boric acid dissolves in water: 1 gram in 18 mL cold water, in 4 mL boiling water, 6 mL boiling alcohol. Powdered boric acid may dissolve more slowly in water than a crystalline product, but with gentle warming will dissolve to give a clear solution.
For the most commonly used TBE buffer, with a pH of 8.3
Store at Room Temp.
Boric acid is a very stable dry solid at room temperature. It should be stable indefinitely, but should be evaluated for continued suitability in user application every three to five years.
Boric acid is a very stable dry solid at room temperature. It should be stable indefinitely, but should be evaluated for continued suitability in user application every three to five years.